- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
New Smart Pimple Patch Clears Acne In 7 Days, Ayurvedic Expert Shares Foods That Heal From Within

Credits: iStock
Waking up to a red, big pimple on your face can be an unpleasant shock that ruins your whole day. Now imagine substituting the ordinary routine of squeezing, covering it up, and waiting for weeks until it goes away with the tiny patch that eradicates the blemish in seven days. That's what scientists have done with the latest "smart" pimple patch — and it might revolutionize acne care entirely.
Dermatologists and researchers have been pursuing quicker, more potent treatments for breakouts for decades. Now, a breakthrough might revolutionize the way we approach breakouts.
Researchers have introduced a new microarray acne patch that doesn't only hide pimples—it effectively eliminates them within seven days. Aside from its acne-clearing potential, this intelligent patch also indicates the possibility of a future where technology like this can administer treatments for ailments far beyond the realm of skin care.
How Does The Smart Pimple Patch Work?
Pimple patches, or acne stickers, are not new. The small hydrocolloid-based bandages have been around for years and were intended to pull out excess oil and water from a pimple and protect it from outside bacteria. Some of them contain medications such as salicylic acid or tea tree oil to accelerate healing.
But there are limits to traditional patches. They primarily work on the outer layer of the skin, give only partial solution, and tend to migrate very easily, particularly at night. For individuals with intractable acne, they're more regarded as a "quick fix" rather than a genuine cure. This is where the new patch based on microarray technology differs.
The study, published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, introduced a patch built on a microarray platform—tiny, spike-like structures designed to penetrate the skin’s outer layer and deliver active ingredients directly into pimples.
What distinguishes this patch from others is the design. Rather than smooth spikes that move or irritate skin, researchers employed arrowhead-shaped micro-spikes manufactured using 3D printing. This design enables the patch to "lock on" so that the ingredients in the patch designed to combat acne reach their destination.
The foundation of the patch is composed of hyaluronic acid, a skin care staple for hydration and repair. Within this base, the researchers added two groups of active ingredients:
Day 1 (Antibacterial phase): Salicylic acid and Cannabis sativa extract to destroy bacteria that cause acne and lower oil.
Day 2–7 (Anti-inflammatory phase): Niacinamide and chamomile extract to soothe redness, decrease lesions, and avoid scarring.
The microarray spikes dissolved into the skin in only 30–90 minutes without causing any irritation or residue.
An 81% decrease in acne lesions within three days and total pimple clearance on day seven. Sebum production also fell dramatically, tackling one of the root causes of acne.
Even better news, 95% of the participants were satisfied with the result, experiencing no pain, irritation, or scarring.
"Our research demonstrates the versatility of microarray patches as a platform for uses other than acne therapy, from skin diseases to obesity treatments and vaccine administration," says Kim.
Why Pimple Patches Became Popular?
Anybody who has ever awoken to a red, inflamed pimple can understand the dread it inspires. Old-school pimple patches—the small, sticker-like band-aids—became a quick fix. They usually soak up oil, minimize moisture, and serve as a protective barrier from picking and bacteria. Some have healing or antibacterial properties.
But although these patches facilitate speedy healing, they don't heal fast enough and frequently don't succeed against resistant, inflamed breakouts. The new study hopes to do better by transforming an ordinary acne sticker into a medical delivery system.
How To Naturally Get Acne-Free Skin Without a Pimple Patch?
Acne is more than just a cosmetic issue. Acne strikes approximately 50 million Americans each year, making it the most prevalent skin disorder in the world, states the American Academy of Dermatology. It may cause emotional anguish, poor self-esteem, and in extreme situations, depression.
Skin care innovations are important, but several experts emphasize that acne isn't skin-deep only. Shweta Shah, Celebrity Ayurvedic Nutritionist, tells how ancient wisdom perceives breakouts differently, "Acne in Ayurveda is not just a skin disease but an indicator of imbalance within. It is frequently associated with an overabundance of pitta dosha—the fire element of the body. When pitta grows perturbed, heat and inflammation increase, and toxins set up shop as pimples." Her treatment aims to cool, cleanse, and balance from the inside out.
Juices That Cool the Body
- Coriander + Amla Juice: Cools pitta, promotes skin repair.
- Cucumber + Mint Juice: Hydrates, inflammation-reducing.
- Aloe Vera + Coconut Water: Calms digestion, toxins flush.
Lifestyle Habits for Clear Skin
- Have warm water with trikatu (ginger, black pepper, long pepper) post-meals for digestion.
- Sleep early before 10 PM to permit natural skin repair.
- Steer clear of spicy, oily, fried food. Opt for cooling foods such as steamed vegetables, moong dal khichdi, and fruits such as pomegranate and papaya.
For local treatment, Shah recommends a Neem + Turmeric paste with rose water to address bacteria and inflammation.
Her recommendation points out a glaring fact: despite advancements in technology, healthy skin may start from within balance.
The intelligent acne patch is more than a cosmetic. It is a reflection of an emerging trend toward tailored, non-surgical medical treatments that may be administered through the skin both safely and effectively. For acne victims, it may mean quicker results without the nastier side effects of oral medications.
And if the same technology can deliver therapies for obesity, chronic skin diseases, or even vaccines, then why can't a simple patch could replace pills or injections.
Standard acne treatment tests patience, as changes are not always apparent for weeks or even months. For most people, that wait time spawns anxiety and frustration, perpetuating feelings of shame about appearance. Something that heals in days, however, provides more than a clearer complexion. It provides relief, confidence, and empowerment.
Mental health experts tend to point out that skin conditions such as acne are not merely skin-deep. Being able to observe concrete improvements within a week might help alleviate the emotional impact of acne, contributing to both mental health and self-esteem.
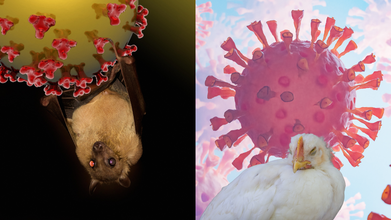
Nipah vs Bird Flu in India: Which Virus Poses A Greater Threat To Humans?
Credits: Canva
As India steps into 2026, two familiar yet unsettling names have returned to the public health conversation. Nipah virus cases reported from West Bengal and fresh bird flu detections among crows in Bihar have raised questions about how dangerous these infections really are for humans. While both diseases originate in animals and can cross over to people, their risks, spread patterns and fatality levels are very different.
Two zoonotic threats, very different risks
Nipah virus and avian influenza are both zoonotic, meaning they jump from animals to humans. Beyond that similarity, the comparison largely ends. Nipah is rare but extremely lethal when it infects humans. Bird flu, on the other hand, spreads widely among birds and poultry, but only occasionally infects people.
Health experts note that understanding this distinction is crucial. Nipah alarms public health systems because even a small cluster of cases can lead to severe illness and death. Bird flu triggers large scale surveillance mainly due to its impact on poultry and the economy, with human cases remaining uncommon.
Read: Bird Flu In India: How Safe Is It To Eat Chicken And Eggs?
Nipah virus and why it worries health officials
The Nipah virus was first identified in Malaysia in the late 1990s and has since caused multiple outbreaks in South and Southeast Asia. Fruit bats are its natural carriers, and humans can get infected through contaminated food, contact with infected animals or close contact with an infected person.
Symptoms often begin like a common viral illness, with fever, headache and cough. In many patients, the disease progresses rapidly. Within days, some develop encephalitis, seizures, confusion and coma. Respiratory distress is also common in severe cases.
According to the World Health Organization, Nipah’s fatality rate ranges between 40 and 75 percent, depending on the outbreak and access to timely medical care. There is no approved vaccine or specific antiviral treatment. Doctors rely on intensive supportive care, which makes early detection and isolation critical.
In January 2026, West Bengal reported multiple Nipah cases, prompting contact tracing and monitoring of nearly 200 people. Most tested negative, and the WHO assessed the risk of wider spread as low. Still, the high death rate keeps Nipah firmly on India’s list of priority pathogens.
Bird flu and its limited human impact
Bird flu, or avian influenza, is caused by influenza A viruses that primarily infect birds. Strains such as H5N1 and H9N2 have been detected repeatedly in India among poultry and wild birds. Bihar’s Darbhanga district recently reported thousands of bird deaths, triggering containment measures.
Humans usually get infected through close contact with sick or dead birds or contaminated environments. When infection does occur, symptoms can resemble seasonal flu at first, but severe cases may progress to pneumonia or acute respiratory distress.
Some bird flu strains have shown high fatality rates among confirmed human cases, sometimes close to 50 percent. However, experts stress that these numbers come from very small case counts. Sustained human to human transmission remains rare, which limits large outbreaks in people.
Read: Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: Myanmar Airport Tightens Health Screenings
Which virus is deadlier for humans?
In terms of individual risk, Nipah virus is considered deadlier for humans. Its consistently high fatality rate, lack of treatment options and potential to cause severe brain inflammation make it especially dangerous, even when case numbers are low.
Bird flu poses a broader threat to animal health and livelihoods, but its direct impact on human life has so far been limited. Public health officials continue to monitor both closely, knowing that vigilance, early reporting and strong surveillance are the best tools to prevent either virus from spiralling into a larger crisis.
Can H5N1 Virus Infect Humans?

Credits: Canva
After the death of 150 crows in Bihar's Bhagalpur district in Naugacha, sudden death of 1,500 crows in Chennai, in Tamil Nadu has again raised concerns over bird flu. At the center of all these is Highly Pathogen Avian Influenza or the HPAI, which is also known as bird flu or the A H5N1 virus. While the strain is known for being notorious and have jumped states, spreading outbreaks in many Indian states, including Jharkhand, Bihar, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Telangana, and Tamil Nadu, the concerns do not end there. Many are concerned if it is a threat to humans too.
Can H5N1 Virus Infect Humans?
As per the World Health Organization (WHO) data, between January 2023 and December 2025, a total of 993 human cases of avian influenza were reported in 25 countries. Almost half of them, which is around 477 people, died. The virus has a fatality rate of 48 per cent.
Two different studies, one done by the universities of Cambridge and Glasgow that show how avian flu strains are multiplying even when the body temperatures could hinder viruses. Whereas, another important study led by Indian scientists, by Philip Cherian and Gautam Menon of Ashoka University, published in BMC Public Health predict if H5N1 or the bird flu virus, could start spreading among humans. How quickly must we act to stop it?
Can H5N1 Virus Infect Humans? How It Survives In The Body?
Human influenza viruses infect many each year. The seasonal strains we see most often fall under influenza A and tend to do well in the cooler temperatures of the upper respiratory tract, which is close to 33°C. They are less suited to the warmer, deeper parts of the lungs, where temperatures reach about 37°C.
As per Science Daily, when the body cannot slow an infection, the virus continues to multiply and spread, which can lead to more serious illness. Fever acts as a protective response, pushing body temperature as high as 41°C. Until now, the exact reason why fever slows some viruses but not others has been unclear.
Avian influenza behaves differently. These viruses usually grow in the lower respiratory tract, and in their natural hosts, such as ducks or seagulls, they often infect the gut. Temperatures in these areas can reach 40°C to 42°C, which helps explain their greater tolerance to heat.
Read: Could Bird Flu Become The Next Pandemic For Humans?
Can H5N1 Virus Infect Humans? What Does The India Specific Study Reveal?
Using BharatSim, an open-source simulation platform originally developed during Covid-19, the researchers recreated what an outbreak might look like in real life. “The threat of an H5N1 pandemic in humans is a genuine one,” Prof Menon said, “but we can hope to forestall it through better surveillance and a more nimble public-health response.”
Their model begins where experts believe a real outbreak would: with a single human infection, most likely a poultry worker or someone exposed to infected birds at a farm or market. The danger, the researchers argue, lies not in that first case, but in whether sustained human-to-human transmission takes hold.
The study by Ashoka University has the most sobering findings in how fast control can slip away. According to the simulations, once cases rise beyond roughly two to ten people, the virus is likely to move beyond immediate contacts and into the wider community.
If households of close contacts are quarantined when just two cases are detected, the outbreak can almost certainly be contained. By the time ten cases are identified, however, the model suggests the infection has probably already spread far enough that early interventions no longer make a meaningful difference.
To ground their work in reality, the researchers focused on a village in Tamil Nadu’s Namakkal district, one of India’s largest poultry hubs. With more than 1,600 farms, around 70 million chickens and tens of millions of eggs produced daily, the region reflects the kind of dense human-animal interaction where spillovers are most likely.
In the simulation, the virus spreads outward from a single workplace into homes, schools and markets, tracking primary and secondary contacts. Once “tertiary” infections, contacts of contacts, appear, control becomes dramatically harder without severe measures such as lockdowns.
Read: Bird Flu Variant Can Now Withstand Fever, Sparking Stronger Human Threats
Can H5N1 Virus Infect Humans? What Works And What Does Not Work
Culling birds work, but only if it happens before humans are infected. Once the spillover is done, isolating patients and quarantining is the only option that can stop the virus, that too if done very early. Targeted vaccination could help raise the threshold at which the virus can sustain itself. Quarantine imposed too early keeps families together longer, increasing household transmission. Imposed too late, it barely slows the outbreak at all.
Does Bigger Penis Help You Ski Better? Why Olympians Are Injecting Hyaluronic Acid - Explained

Credits: Canva
What won't people do to get that gold. In the quest for so, Olympians re injecting hyaluronic acid in their penises. The reason? For skiing, it helps them fly better and further.
In January, a German newspaper, Bild reported that jumpers were injecting, what now is dubbed as Penisgate in their penis. The newspaper claimed that athletes inject the acid in the penis before they are measured for their suits.
Does Bigger Penis Help You Ski Better?: What Does Penisgate Do To The Penis?
Hyaluronic acid is used for cosmetic surgery, especially as a filler. Surgeons have also used it for penile girth enlargement. This is exactly why it is being used by the Olympians.
Injecting hyaluronic acid will increase the penile girth. However, experts point out that this means, one has to insert a lot of it in the penis to have this worked out. It is not a permanent solution, and can only last up to six to 12 months, depending on the absorption.
Inserting this will increase the penile girth or the penis circumference by one or two centimeters. As per the International Ski and Snowboard Federation, FIS, the surface area of their suits during competition could be increased by this, which increases their flight in the air, reported BBC.
"Every extra centimetre on a suit counts. If you suit has a 5% bigger surface area, you fly further," said FIS ski jumping's men race director Sandro Pertile, reported by BBC.
Does Bigger Penis Help You Ski Better?: Why Are Olympians Injecting Their Penises With Hyaluronic Acid?
Ahead of each season, ski jumpers undergo measurements using 3D body scanners and are required to wear only elastic, body-tight underwear during the process.
Regulations allow suit measurements a tolerance of just 2–4 cm. As part of this assessment, athletes’ crotch height is also recorded. The suit’s crotch height must match the athlete’s own measurement, with an additional 3 cm permitted for men.
Hyaluronic acid injections into the penis can last for up to 18 months.
Athletes have previously faced scrutiny for attempting to boost performance through alterations or manipulation of their suits.
Does Bigger Penis Help You Ski Better?: What Are The Risks Of Injecting Hyaluronic Acid In Penis?
Experts caution that penile injections using hyaluronic acid can pose serious short- and long-term risks.
They warn that improper technique or incorrect dosing may lead to pain, disfigurement, deformity, infection, inflammation, altered sensation, and sexual dysfunction. In rare cases, infections can worsen, causing tissue death (gangrene) and even loss of the penis.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

