- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
A ‘Super Flu’ K-Strain Is Raising Early Christmas Alarms, Here’s What We Know

Credits: Canva
Super flu or the mutated variant of flu, clade K, has swept the world and caused an early spike in cases worldwide. In Australia, it has caused an early summer spike, while in the UK, it has caused a surge in hospitalization. As per the National Health Service (NHS) England, the number of cases of K flu has been increasing since December 7 and December 11. Hospitalization is up 55% in a week, noted NHS.
This has led to a warning by the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) and urged anyone with symptoms to "consider wearing a mask". In Australia too the rise of cases has led to health warnings among people. President of the Royal Australian College of General Practitioners Michael Wright said, "We’re diagnosing more cases of the flu than ever, and it is concerning that our vaccination rates have been falling year on year for the past few years. If you have got the flu, make sure you don’t go spreading it to other people because that’s not the gift that people want at Christmas"
What Do We Know About The Subclade K or the Super Flu So Far?
Known as the superfly, this is H3N2 'subclade K'. It is a type of seasonal influenza A virus and people have not encountered much of it in the recent years. This is why there is less immunity against it. However, the National Health Service (NHS), UK, has already sent out a 'flu jab SOS' to vulnerable people.
NHS has confirmed that the super flu is circulating in England this year, and due to less immunity, it is making it easier to spread across people. The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has urged people to get a flu jab. As per the early data, this year's vaccine has offered good protection despite the new strain.
Daniel Elkeles, chief executive of NHS Providers, said that the major concern is that H3N2 is associated with a more severe illness and superflu could be "a very nasty strain of flu". He said that UK could be experiencing a "tidal wave" of illness.
The main strain circulating this winter is a drifted H3N2 variant, which the UKHSA says has left the community with “less natural immunity.” H3N2 strains tend to cause more serious illness in older adults than H1N1 strains and are linked to higher hospitalizations and deaths. This pattern adds further strain to the NHS during the winter months.
Current data shows that 71.7% of people aged 65 and over in England have received this year’s flu vaccine as of December 7. Uptake remains lower in those under 65 in clinical risk groups (37.4%), pregnant women (35.6%), and children aged two or three (41.9%).
Should You Get A Vaccine?
You should. NHS UK, and National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance Australia are urging anyone with symptoms, or anyone who is vulnerable or eligible to get an influenza vaccine.
Even if you are healthy, you should get the shot, say doctors. Vaccines are still working against the drifted influenza A (H3N2) subclade, also known as the super flu. The vaccines in high street chemists are sold for £20.
Anyone can be vaccinated, except for those who have a serious allergy to any of its ingredients or to the vaccine it self. The best way to know is to speak to the pharmacist and your GP.
For the vaccine to work, it usually takes up to 14 days. However, what is more important to not is that during the 14-day-long period, you are still vulnerable to catching the virus.
Flu Vaccine Myth 101: Some people think that it is the flu vaccine itself that has given them the flu, however, the truth is that while vaccine does not give you a flu, it gives your body the instruction it needs to fight off an infection, in case you catch it. While you may still catch the flu after being vaccinated, the affects will be milder and would not last as long.
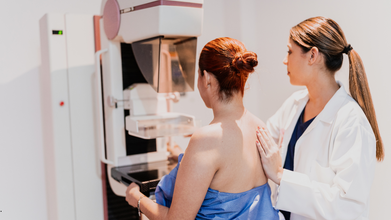
AI Detects More Breast Cancer Cases in Landmark Swedish Study
Credit: Canva
Using artificial intelligence (AI) in breast cancer screening can reduce the number of cancers diagnosed in late stages by 12 percent, according to a major new study from Sweden.
The study found that fewer women in the AI group were diagnosed with breast cancer in the years after screening. There were 1.55 cancers per 1,000 women in the AI-supported group, compared with 1.76 per 1,000 in the standard screening group.
According to lead author Dr Kristina Lang of Lund University in Sweden, this indicates better early identification of clinically relevant cancers. She said of the results: “Our findings show that AI-supported screening improves the early detection of breast cancers that are more likely to become aggressive or advanced.
“This results in fewer serious cancers being diagnosed in the interval between screenings.”
She added that wider adoption of AI-supported mammography could ease workforce pressures on radiologists while improving early detection, including of aggressive cancer subtypes.
What Did The Study Find?
The study, published in The Lancet, involved around 100,000 women who took part in routine mammography screening between April 2021 and December 2022, making it the first large randomised trial to assess how AI performs in real-world breast cancer screening.
Women were randomly divided into two groups. One group received standard screening, where mammograms were read by two radiologists and the other group had AI-supported screening, where an AI system assessed the scans first.
Low-risk cases were read by one radiologist, while higher-risk cases were checked by two, with the AI also flagging suspicious areas.
The results showed that 81 percent of cancers in the AI-supported group were detected during screening, compared with 74 percent in the standard screening group—a nine percent increase. Importantly, false-positive rates remained similar, at 1.5 percent in the AI group and 1.4 percent in the control group.
Despite positive results, Dr Lang cautioned that introducing AI into healthcare must be done carefully, using validated tools and continuous monitoring to understand how performance may vary across regions and over time.
READ MORE: This 2 Hour Activity Can Reduce Your Breast Cancer Risk, Study Shows
Breast Cancer: A Rising Crisis
About 1.9 lakh Indian women are diagnosed with breast cancer annually, meaning that a new case is diagnosed every four minutes. On average, a woman in India dies of breast cancer every eight minutes, highlighting how urgently the country needs stronger awareness, early diagnosis and sustained care.
One factor that sets India apart is the age at which women are affected. Almost half of all breast cancer patients in the country are younger than 45. This is a much higher proportion than seen in many Western nations, where the disease is usually detected later in life.
Moreover, sedentary habits, excessive consumption of processed foods as well as alcohol and smoking promotes obesity and hormonal changes which pave the way for breast cancer development.
Union Budget 2026 Agriculture Push Will Improve Public Health, Experts Say

Credit: Canva
During today's Union Budget, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced multiple initiatives and a staggering ₹1,62,671 crore to increase agricultural production in the country
Sitharaman, who was presenting her ninth consecutive budget, said the government will support the growth of high-value crops such as coconut, sandalwood, cocoa and cashew in coastal regions, agarwood in the North East and nuts,s including walnuts, almonds and pine nuts.
Dedicated programmes will focus on rejuvenating old orchards, expanding high-density cultivation and promoting value addition by engaging rural youth, while new coconut promotion schemes aimed at boosting productivity will be launched.
She noted: "India is the world’s largest producer of coconuts. About 30 million people, including nearly 10 million farmers, depend on coconuts for their livelihood. To further enhance competitiveness in coconut production, I propose a Coconut Promotion Scheme to increase production and enhance productivity through various interventions 16 including replacing old and non-productive trees with new saplings/plants/varieties in major coconut growing states.”
And health experts across the country say that an increase in consumption of these food items can significantly help improve your health.
Dr Sunil Kutty, Director and Consultant Brain and Spine Surgeon, NewEra Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, exclusively told Healthandme: "The Union Budget emphasises improving national nutrition and food security, recognising that better diets are foundational to health and well‑being.
"By strengthening food systems, supporting high‑value crops and enhancing access to nutrient‑rich foods, the government aims to reduce malnutrition, micronutrient deficiencies and diet‑linked diseases like Type-2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases. Integrating nutrition‑focused initiatives with healthcare can lower the overall burden of non‑communicable conditions and improve immunity, especially among children, women and vulnerable groups.
"These measures also support rural livelihoods, increasing access to affordable, healthy food across socio‑economic groups, contributing to long‑term health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs."
Coconut: Prevents Cell Damage And Packed With Essential Minerals
When eaten in moderation, coconuts offer healthy fats (MCTs), fibre, manganese, copper, iron, potassium as well as ample of antioxidants. Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body and potentially lowers blood pressure, while the fruit's high fibre content supports bowel health and prevents constipation.
Coconuts are also especially high in manganese, which is essential for bone health and the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and cholesterol. Along with this, they’re also rich in copper and iron, which help form red blood cells, as well as selenium, an important antioxidant that protects your cells and reduces cell damage which can prevent future cancer development.
A 2020 case study found that supplementing with coconut oil helped lower blood sugar levels in a person with diabetes, a condition characterized by unstable blood sugar levels. The researchers suggest that these effects may be due to the coconut’s anti-inflammatory properties and antioxidant content.
A 2024 animal study also found that consuming coconut water after eating could help manage blood sugar levels. This could be due to bioactive compounds like ellagic acid, butin, and quercetin, among others.
Sandalwood: Skin Benefits and Anxiety Reduction
Sandalwood offers benefits for skin health (acne, ageing, brightening), mental well-being, aid sleep, and possesses anti-inflammatory, antiseptic as well as antibacterial properties, making it useful for skin irritations, respiratory issues, and even potentially lowering blood pressure.
A 2017 Sigma study suggests that lavender, sandalwood, and orange-peppermint aromatherapy helped reduce self-reported feelings in anxiety of 87 women undergoing a breast biopsy.
In a 2016 pilot study published in NPC of 32 people in Vienna, Austria, participants inhaled lavender and sandalwood oil. The study found that the participants’ blood pressure levels were lower and that the cortisol levels in their saliva were lower after the aromatherapy.
Cocoa: Boosts Heart Health
While cocoa is most famous for its role in chocolate production, it is also packed with polyphenols and reduces high blood pressure by improving nitric oxide levels.
Researchers have previously linked polyphenols to numerous health benefits, including reduced inflammation, lower blood pressure and better heart health. It also contains flavanols, which have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
The flavanols in cocoa also improve nitric oxide levels in the blood, which can enhance the function of the blood vessels and reduce blood pressure.
Nuts: Improve Overall Health
Doctors say nuts offer heart-healthy fats, protein, fibre, vitamins, and minerals, which can lower heart disease and diabetes risk, improve cholesterol, reduce inflammation, and support weight management when eaten in moderation as part of a balanced diet.Over time, this can improve artery health, lower bad LDL cholesterol, and reduced risk of blood clots, with varieties like almonds, walnuts, and pistachios providing unique nutrients like omega-3s, antioxidants and selenium.
Lastly, Pattabhi Rama Rao, Managing Director, Gourmet Popcornica also noted to Healthandme: "These measures, combined with stronger market linkages and local enterprise development, can make wholesome foods more affordable and accessible, directly supporting better nutrition and overall public health outcomes across the country. Not just this, farmers being able to access equitable income will enable them to access high-quality, nutritious food.
"By prioritising high-value and nutritious crops like coconut, cashew, cocoa, and walnuts, the government is not just enhancing farmers’ incomes but also ensuring that healthier, nutrient-rich foods are more widely available to the public.
"Diversifying production through fisheries, livestock, and region-specific crops, like maize in Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, will improve access to proteins, healthy fats, and essential micronutrients, which are vital for balanced diets.
Union Budget 2026: FM Nirmala Sitharaman Announces Biopharma Shakti, Medical Tourism. Here Is What Experts Say

Credit: Canva, ANI
During this year's Union Budget presentation, healthcare development took centre stage as Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced an array of proposals aimed at improving medical tourism, yoga and Ayurvedic medicine exports, and 'Biopharma Shakti'.
Sitharaman began presenting this year's budget by noting: "We’re inspired by three kartavyas, first is to accelerate economic growth by building resilience to global turmoil, second is to make people strong partners in prosperity, sabka saath sabka Vikas is the third kartavya."
Here is what she proposed for the improvement of healthcare services in the country:
Biopharma Shakti
The Minister started off by suggesting a ₹10,000 crore outlay for Biopharma Shakti to support domestic medication production for the next five years.
During the session, which mostly focused on the development of Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, she stated that India’s disease burden has begun increasingly shifting towards non-communicable diseases.
To help combat this, Sitharaman said: "To develop India as a global bio-pharma manufacturing hub, I propose Bio Pharma Shakti with an outlay of ₹10,000 crores over the next 5 years. This will build an ecosystem for domestic productions of biologics and biosimilars.
"For domestic production of biologics and biosimilars, the strategy will include a biopharma-focused network with three new national institutes of pharmaceutical education and research, popularly known as NIPERS, and upgrading seven existing ones. It will also create a network of 1,000 accredited India clinical trials sites.
"We propose to strengthen the Central Drug Standard Control Organisation to meet global standards and approve timeframes through a dedicated scientific review and specialists."
By encouraging domestic production of biologics and biosimilars, the government aims to make advanced treatments more affordable and accessible for Indian patients.
The government. is yet to reveal which type of drugs will receive priority during production, whether they will be exported and whether new factories will be set up across the nation.
Speaking of how beneficial this can be for the public, Uday Deshmukh, Chairman & Founder CEO of Onco-Life Cancer Centre, exclusively told Healthandme: "This visionary initiative comes at a critical juncture, as India faces a growing burden of chronic and complex diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
"The proposed investment over the next five years will significantly strengthen domestic biopharmaceutical research, innovation, and manufacturing, making advanced cancer therapies more accessible and affordable.
"By accelerating clinical research and precision medicine while reducing import dependence, Biopharma Shakti has the potential to transform cancer care outcomes and build a truly self-reliant healthcare ecosystem for India.”
Import Duty Decreased On Cancer Drugs
Cancer drugs are medications, including chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and hormone therapies, used to kill cancer cells, slow growth, or relieve symptoms. Some popular medications include Cisplatin, Paclitaxel, Doxorubicin and Pembrolizumab (Keytruda), most of which are imported into India.
These imported, specialized cancer treatments, particularly targeted therapies and monoclonal antibodies, often cost thousands, placing a massive financial burden on patients, leading to lifelong debts.
However, in this year's Union Budget, Sitharaman proposed reducing import duty tax on 17 cancer drugs and seven medicines for rare diseases, which will in turn, help patients seek proper care on a timely basis.
Deshmukh commented: "India is witnessing a steady and alarming rise in cancer cases, where late detection, prolonged treatment and high medicine costs often lead to preventable complications and loss of life. Against this backdrop, the Union Budget’s decision to remove customs duty on 17 cancer drugs and 7 medicines for rare diseases stands out as a truly progressive and patient-first measure.
"Affordability remains one of the biggest hurdles in cancer care, forcing many families to delay or discontinue treatment. By reducing import duties, this move has the potential to significantly lower the cost of advanced and targeted therapies, making them accessible to a larger section of patients."
Increase In Medical Hubs And Institutions
Sitharaman proposed launching a scheme to support states in setting up five regional medical hubs, which will include AYUSH centres and infrastructure for diagnostics and post-care rehabilitation.In addition, ten new allied health disciplines will help train one lakh professionals, strengthening the healthcare support system across hospitals, wellness centres and medical tourism facilities.
Furthermore, she noted that no mental health institutions have been set up in North India and to boost care, the government will set up centres in Ranchi, Jharkhand and Tezpur, Assam.
Namrata Jain, Psychotherapist and Relationship Expert at Out Aloud commended the government's initiative to improve mental health care and told Healthandme: The focus on mental health alongside Ayurveda and wellness in this budget is a powerful affirmation that holistic wellbeing matters. Now is the time to harmonize our ancient Indian sciences with contemporary mental health frameworks to nurture resilient, compassionate communities.
"It feels deeply reassuring to see mental health, Ayurveda and wellness coming together in this budget. Healing has always been holistic and this is our reminder to blend ancient Indian wisdom with modern, trauma-informed mental health practices to support gentler, deeper, more human wellbeing."
Medical Tourism
During her ninth consecutive Union Budget, Sitharam suggested turning India into a 'global medical tourism hub' by supporting states in setting up five regional medical tourism hubs, which are expected to attract international patients, improve healthcare infrastructure and create jobs in allied services.
Pankaj Chandna, Co-Founder, Vaidam Health told this publication: "Union Budget 2026 is pushing medical value tourism from a 'hospital visit” into a full-stack, globally benchmarked care experience. The five regional medical value tourism hubs can standardise patient journeys across diagnostics, treatment, post-care and rehabilitation, while easing pressure on metros by building credible capacity in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
"What stands out this year is the emphasis on technology as a growth lever, especially AI-enabled diagnostics, clinical decision support, patient coordination, and faster turnaround on care pathways, all of which directly improve international patient confidence and outcomes. The parallel focus on strengthening allied health institutions and expanding training capacity is equally important because world-class infrastructure only works when the workforce is future-ready."
Focus on Yoga And Ayurveda
Under Budget 2026-27, 1.5 lakh caregivers will be trained to provide yoga and Ayurveda-based services to improve access to wellness care while also creating large-scale employment opportunities. The proposal reflects the growing demand for traditional and preventive healthcare in India and abroad.
She also proposed setting up new All India Institutes of Ayurveda as part of the government’s push to expand traditional and modern healthcare infrastructure as well as to improve the quality of Ayurveda education and help standardise treatment practices across the country.
"I propose to set up three new All India Institutes of Ayurveda; Upgrade AYUSH pharmacies and drug testing labs and make available more skilled persons; Upgrade the WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre in Jamnagar," said Sitharaman.
Focusing on the connection between traditional Indian medicine and medical tourism, Sonam Garg Sharma, Founder, Medical Linkers told Healthandme: "As a country, we are increasingly recognised for combining clinical excellence with value-driven care, and healthcare hubs that integrate advanced diagnostics, post-treatment rehabilitation, and AYUSH-led wellness therapies such as yoga and Ayurveda can take that advantage further by offering a truly end-to-end patient journey.
"This also adds meaningful momentum to India’s medical value tourism story, where outcomes, experience, and continuity of care matter as much as affordability."
Upgrade In Geriatric And Professional Care
Lastly, Sitharaman added that institutions for allied health professionals will be upgraded and professionals will be trained in the coming year to cover geriatric and allied sectors. New AHP institutes will also be set up in the private and government sectors
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

